Medically Reviewed by Melinda Ratini, DO, MS on December 20, 2020
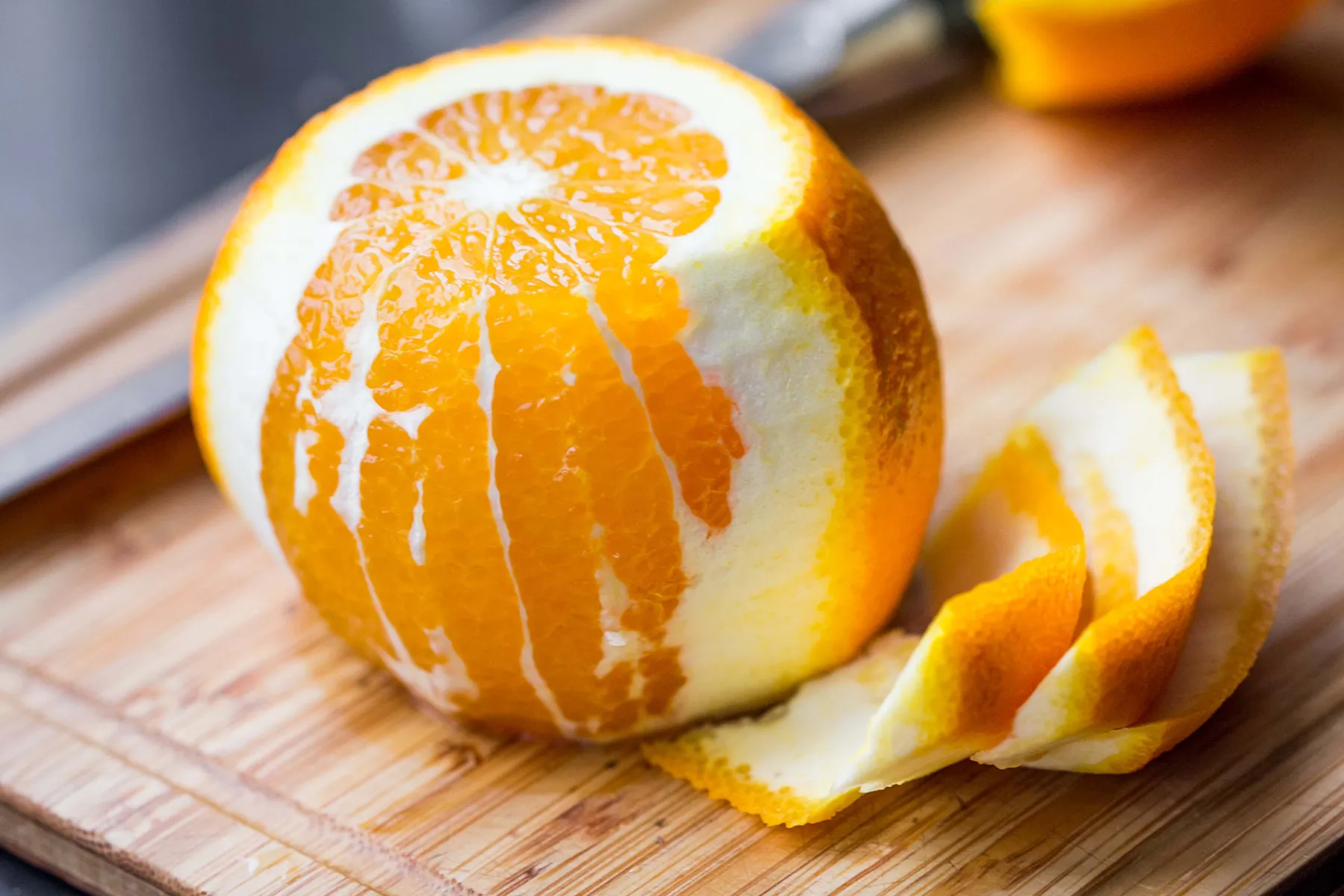

How Much Do You Need?
1/11
If you eat a balanced diet, it’s pretty easy to get enough. Adult women (who aren’t pregnant or breastfeeding) need 75 milligrams of vitamin C per day; men, 90 milligrams. A mere 1/2 cup of raw red bell pepper or 3/4 cup of orange juice will do it, while 1/2 cup cooked broccoli gets you at least halfway there. Your body doesn’t make or store vitamin C, so you have to eat it every day.
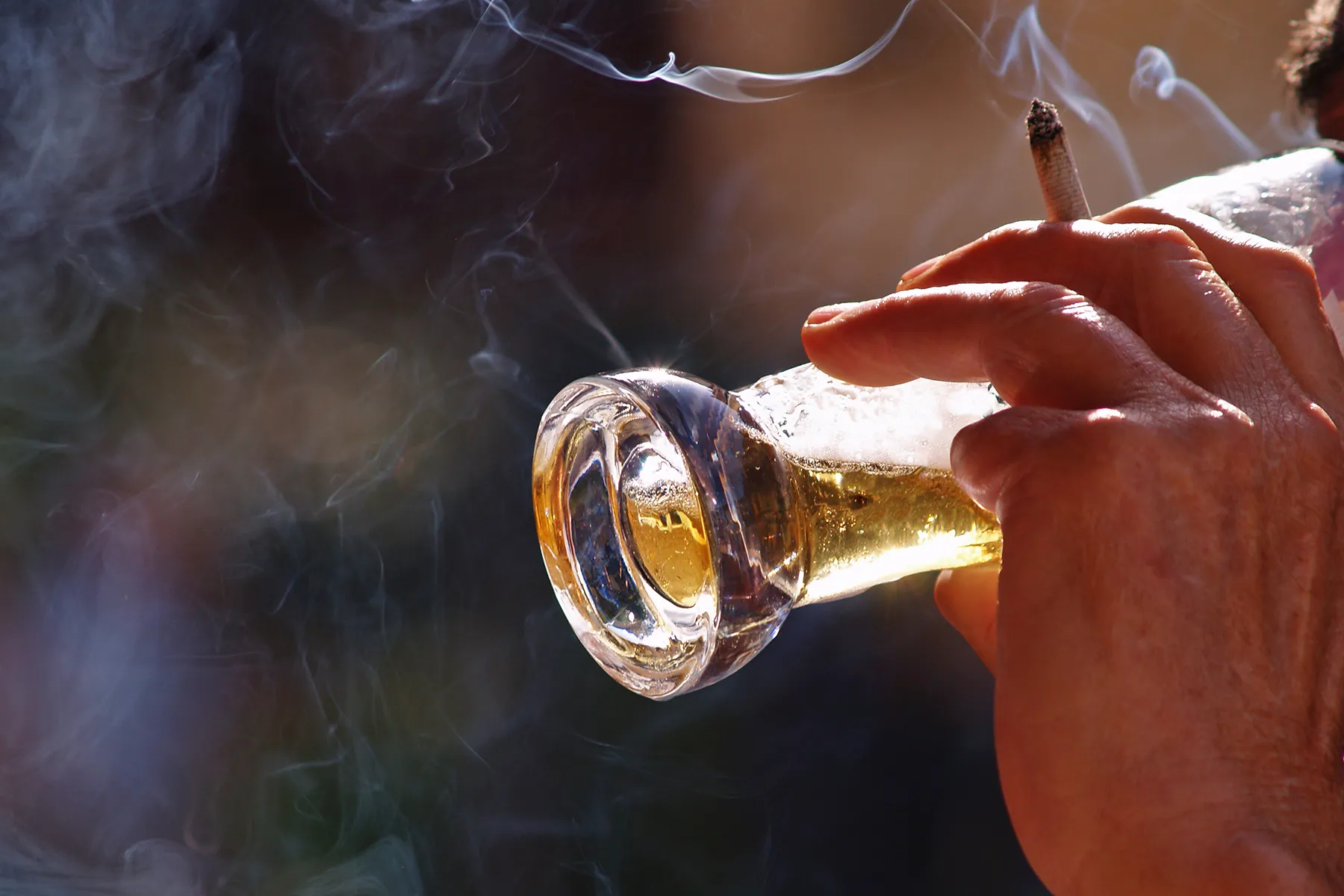

Who’s Falling Short?
2/11
The most likely people include those with an overall poor diet, with kidney disease who get dialysis, heavy drinkers, and smokers. You’ll need an extra 35 milligrams of vitamin C per day to help repair the damage caused by free radicals that form when you smoke. If you’re among the 7% of Americans who aren’t getting enough vitamin C, you’ll notice symptoms within 3 months.
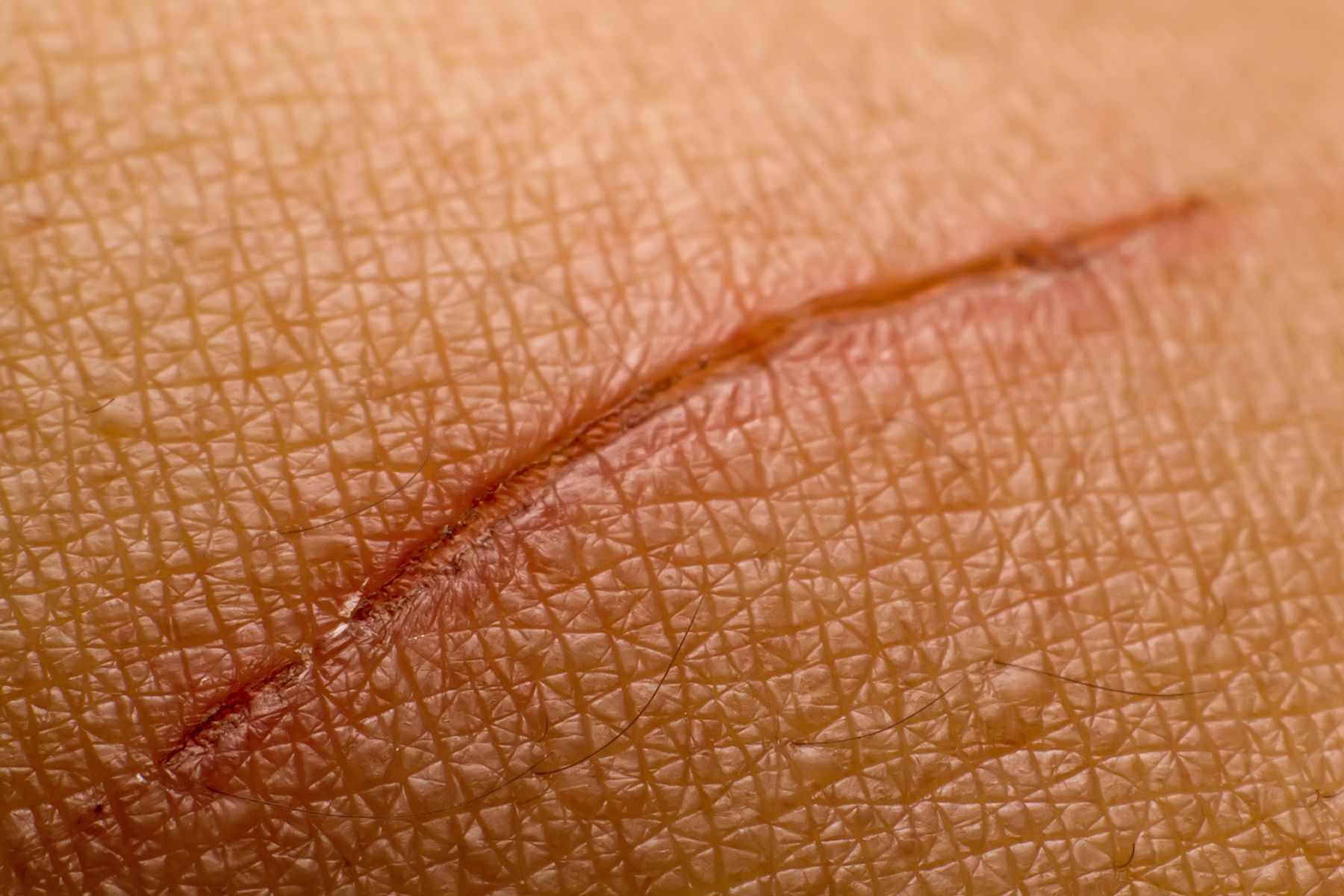
Slow Wound Healing
3/11
When you get hurt, levels of vitamin C in your blood and tissue go down. Your body needs it to make collagen, a protein that plays a role in each stage of repairing the skin. And vitamin C helps neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that fights off infection, work well.
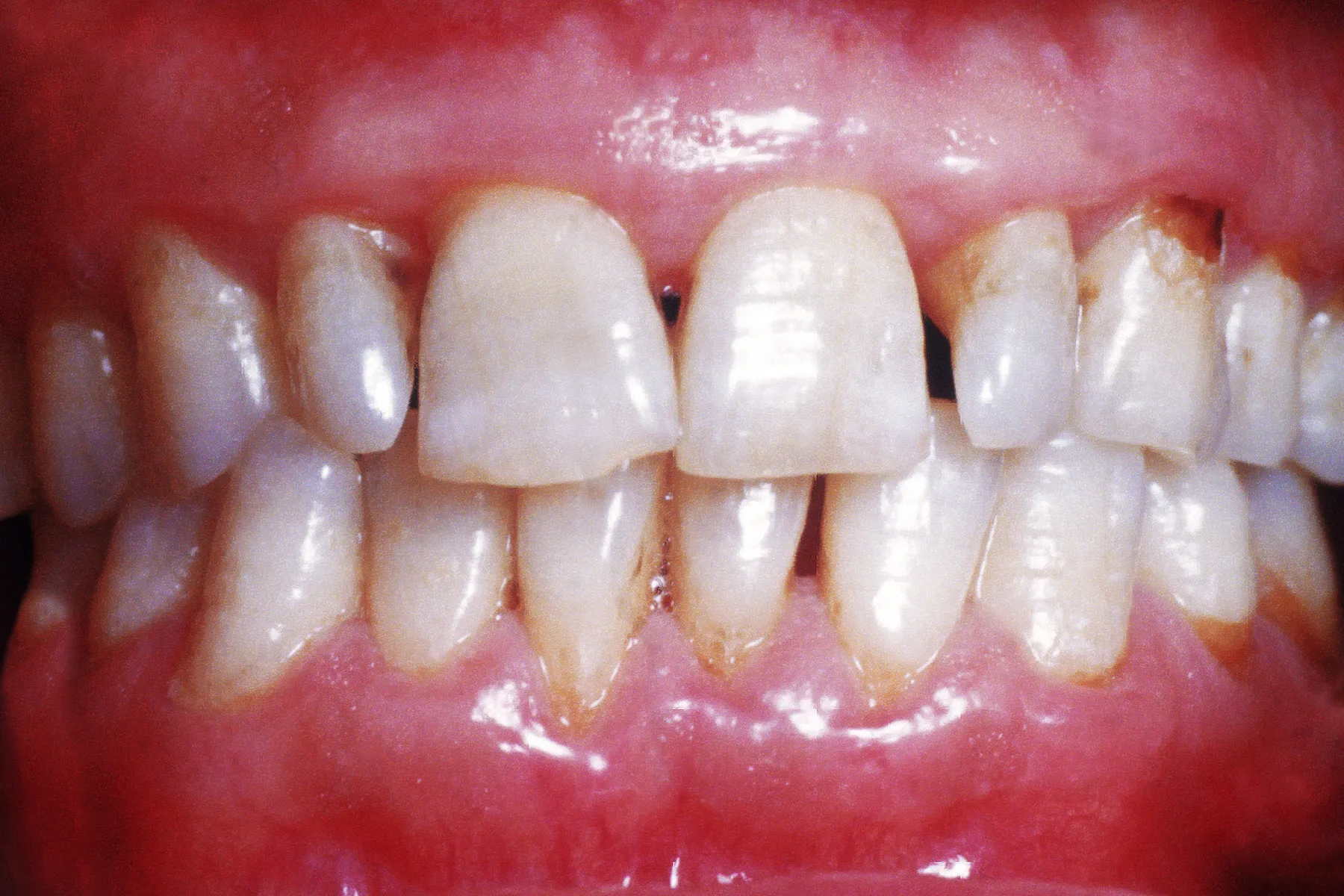
Bleeding Gums, Nosebleeds, Bruises
4/11
Vitamin C keeps your blood vessels healthy, and it helps your blood clot. Collagen is also essential for healthy teeth and gums. One study found that people with gum disease who ate grapefruit for 2 weeks noticed their gums didn’t bleed as much.

Weight Gain
5/11
Early research has found a link between low levels of vitamin C and higher amounts of body fat, especially belly fat. This vitamin may also play a role in how well your body burns fat for energy.
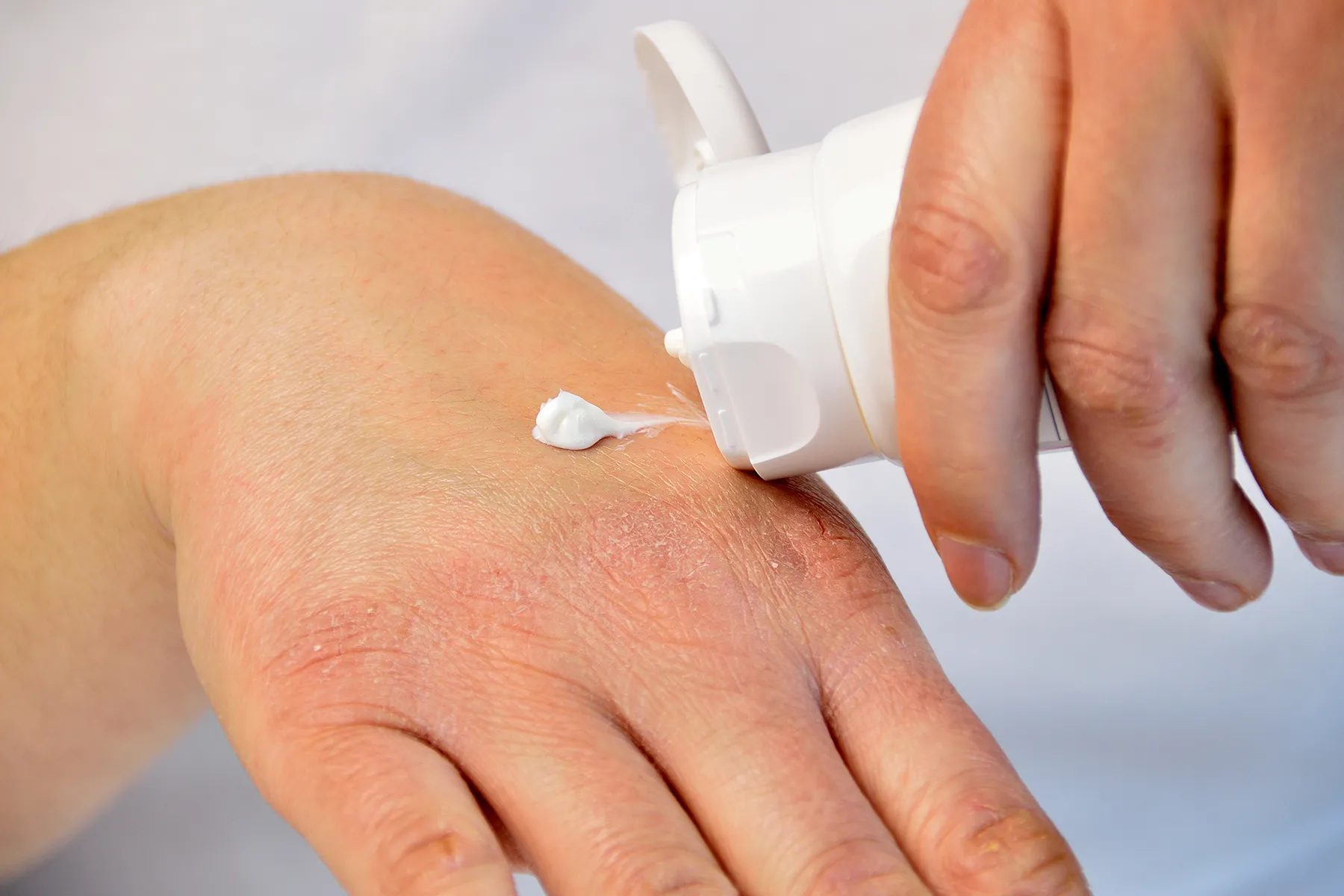
Dry, Wrinkled Skin
6/11
People who eat a healthy diet with plenty of vitamin C may have smoother, softer skin. One possible reason: Because vitamin C is an antioxidant, it can help protect your skin from free radicals. These break down oils, proteins, and even DNA.

Tired and Cranky
7/11
In a very small study, 6 of the 7 men who had low levels of vitamin C said they felt tired and irritable. That suggests a link, though other things could be playing a role. Another study of 141 office workers found that giving them vitamin C made them feel less tired within 2 hours, especially if their level was lower to start with. Then the effect lasted for the rest of the day.

Weak Immunity
8/11
Since vitamin C has several jobs related to your immune system, it shouldn’t surprise you to learn you’re more likely to get sick and may have a harder time recovering. There’s some evidence that vitamin C can help protect you from illness such as pneumonia and bladder infections. It may even lower your odds of heart disease and some types of cancer.

Vision Loss
9/11
If you have age-related macular degeneration (AMD), it may get worse faster without vitamin C and other antioxidants and certain minerals. Getting enough vitamin C from foods might help prevent cataracts, but we need more research to understand that relationship better.
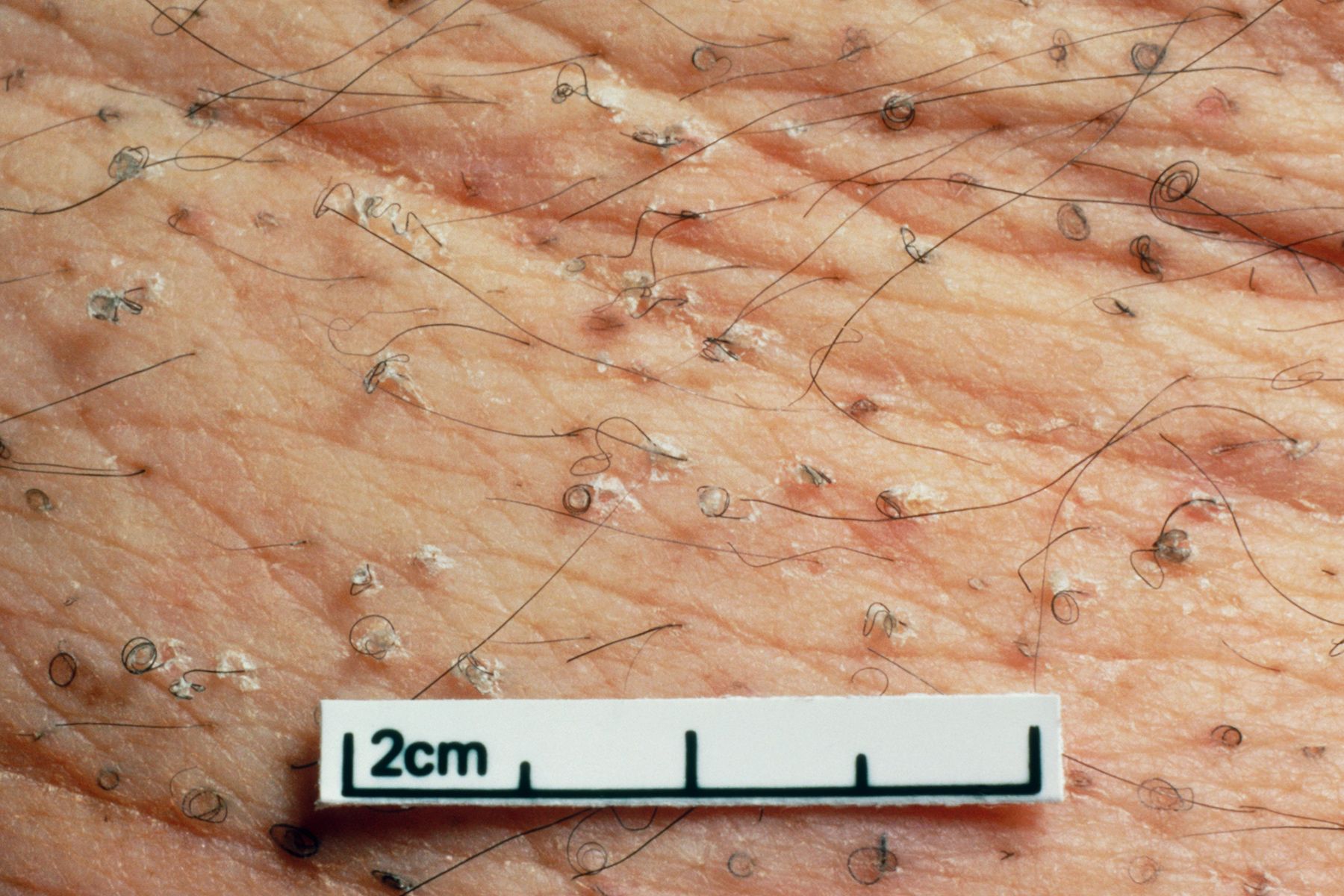
Scurvy
10/11
Before the 1700s, this potentially deadly disease used to be a huge problem for sailors. Today, it’s relatively rare but possible if you get only 10 mg/day of vitamin C or less. People with scurvy also have problems such as loose teeth, cracked fingernails, joint pain, brittle bones, and corkscrew body hair. When you boost vitamin C, symptoms start getting better in a day, and usually it’s cured within 3 months.
